链表基础知识
什么是链表
链表是一种通过指针串在一起的线性结构,每一个节点由两部分组成:数据域和指针域(用于存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个指针域指向null(空指针)
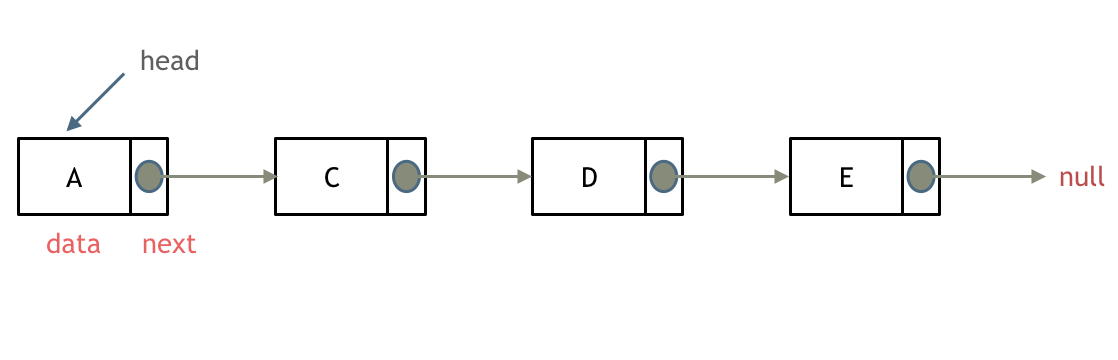
[head:链表头节点,链表入口节点]
链表的存储方式
链表不是连续分布的【区别于数组】,链表是通过指针域连接在内存中的节点,所以链表中的节点在内存中不是连续分布的,而是散乱分布在内存中的某地址上的,分配机制取决于操作系统的内存管理
链表方法
- 创建链表
- 插入节点
- 末尾插入——push(val)
- 链表为空——添加第一个元素
- 链表不为空——追加元素
- 任何位置插入——insert(val, position)
- 移除元素
- 根据位置移除——removeAt(position)
- 根据元素值移除——remove(val)
- 拓展
- 查找是否存在val的节点——indexOf(val)
- 链表是否为空——isEmpty()
- 链表长度——size()
- 获取链表节点值——toString()
单链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
| class NodeList{
constructor(val, next) {
this.val = val ? val : undefined;
this.next = next ? next : null;
this.count = 0;
}
push(val) {
const node = new NodeList(val, null);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
let current = head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
};
current.next = node;
};
}
getElementAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let node = this.head;
while (index--) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return undefined;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
const previous = getElementAt(index -1);
const current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.val;
}
return undefined;
}
insert(val, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
const node = new NodeList(val, null);
if (index === 0) {
const current = this.head;
node.next = current;
this.head = node;
} else {
const previous = getElementAt(index -1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
indexOf(val) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.count && this.count !== null; i++) {
if (current.val === val) {
return i;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
};
return -1;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.size();
}
toString() {
if (!this.head) return '';
let objString = `${this.head.val}`;
let current = this.head.next;
while (current) {
objString = `${objString},${current.val}`;
current = current.next;
};
return objString;
}
}
|
双向链表
双向链表和普通链表的区别在于:
在链表中,一个节点只有链向下一个节点的链接;而在双向链表中,链表是双向的:一个链向前一个节点,一个链向后一个节点
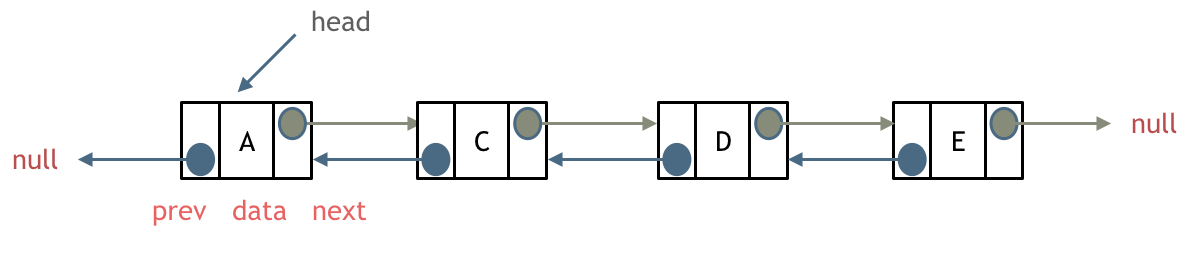
双向链表不用next而用prev和tail指针代替
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| class DoubleNodeList {
constructor(val, prev, tail) {
this.val = val ? val : undefined;
this.prev = prev ? prev : null;
this.tail = tail ? tail : null;
this.count++;
}
getElementAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let node = this.head;
while (index--) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return undefined;
}
insert(val, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoubleNodeList(val, null, null);
let current = head;
if (index === 0) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (index === this.count) {
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else {
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.count === 1) {
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = undefined;
} else {
current = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
const previous = current.prev;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
this.count--;
return current.val;
}
return undefined;
}
}
|
循环链表
循环链表可以向单链表一样引用,也可以像双链表一样引用,特点在于最后一个元素指向链表中的某一个节点,而不是null
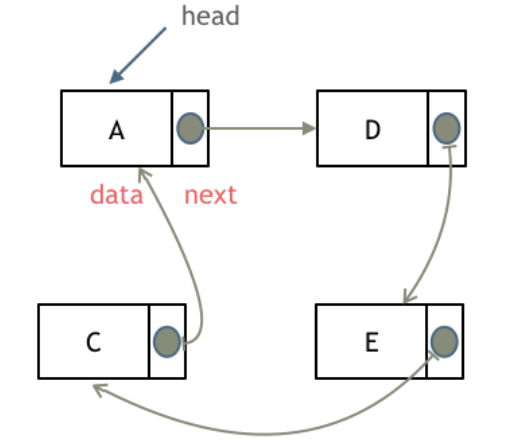
有序链表
有序链表指元素有序的链表结构
参考
代码随想录_链表



